We have updated the content of our program. To access the current Software Engineering curriculum visit curriculum.turing.edu.
Express Middleware
Goals
- Understand what middleware functions are and when they are used
- Recognize common use cases for middleware functions on a high level
- Implement middleware functions and apply them to your Express server endpoints
Getting Started
Clone down this repo, run npm install, and start the server to make sure it is set up correctly. You should see something like this in your terminal:
Middleware exercise server running on http://localhost:3000
Express Middleware
What is it?
Middleware got the name because it is a regular JavaScript function that is run in the middle of your request. So a request is received by your server and before it gets to the route handler (the endpoint), Express will run any middleware for that endpoint.
We can take it step-by-step:
- The server receives a request with an HTTP verb, URL, headers, and body
- If there is a middleware function that should run after the request is received, it does so at this time
- The middleware function runs and either send a response or passes control to the next middleware function
- If there are no middleware functions left, then the control is passed to the route handler
Stop and Think
- Have you used any middleware functions in your previous projects?
- How did you implement the functionality?
Here is a flow diagram of middleware functions. It shows how control is passed from the request through the response. Each middleware function has the ability to send a response early before the request gets to the main route handler.
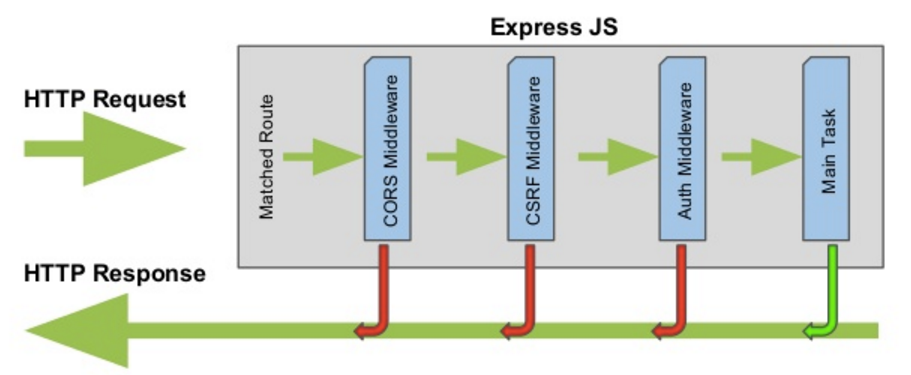
The names for the middleware functions in the picture above are some other use cases for middleware. At this point, you should be pretty familiar with CORS which allows specific domains outside from your API to request access to specific resources. But what about the others?
CSRF (Cross-site Request Forgery)
CSRF is a type of malicious exploit of a website where unauthorized commands are transmitted from a user that the web application trusts. This deals with an applications security in which an innocent user that has authorization to that website is tricked into submitting a request that he did not intend. This can be done through hidden forms, automatic-action HTML image elements, and email spam amongst others. Middleware that utilizes different types of tokens can be applied to help protect against this.
Auth Middleware
Auth middleware deals with the authentication of the request and checking to see that the user has access to completing this functionality. As expected, you likely don’t want just anyone to be able to add/remove your valuable data on your application. In the same respect, you likely don’t want a user having edit access to another user’s settings. This can be implemented in multiple ways through things like OAuth and other types of tokens which is beyond the scope of this lesson, but know that this exists and is a common type of middleware used.
Other Middlewares
Some other common uses of middleware can include error handling. Express has a built in error handler for any unhandled errors that may have occurred throughout the pipeline. There is also middleware that can be used to handle routes for your application. Remember app.use(express.static('public'))? If you are serving your frontend from your backend application including static files like HTML, CSS, & JS, you can have Express render different views based on different HTML files (similar to how something like React Router functions). This could be useful for pages where a user isn’t authorized or a page that doesn’t exist.
Getting Started
As a primer, read through the introduction on this Express documentation page and the first example under the section “Application-level middleware”.
You Turn
Turn to someone next to you and talk about the documentation you just read. What does a middleware function look like and how do you apply a middleware function to all endpoints? A single endpoint?
Bonus: How can you have multiple middleware functions be reusable for an endpoint?
Note
If you are curious to learn more about Express’s error handling and routing middleware, you can see some examples of how this is used on this page as well!
First Middleware
In the server file, there is a commented section something like this:
// 1. First middleware function (apply this function to all endpoints)
// Log data about the request:
// HTTP verb, endpoint, data in the request body, and headers!
Just below these comments, create a new function using the Express middleware syntax from the documentation page.
Start small - create a function that console logs something, apply the middleware function to all of the endpoints, and test a request. Then add the functionality listed in the comments.
Second Middleware
Next, in the server file there is a commented section something like this:
// 2. Second middleware function (apply to only endpoint POST /pets)
// Check that there has been information sent in the request body
// If there is a request body, continue to POST request handler
// If there is not a request body, do not continue and send 422 response
Again, create a function that starts small by console logging, apply the middleware only to the POST request, and test a request. Then add the functionality listed in the comments.
Third Middleware
Finally, in the server file there is a commented section something like this:
// 3. Third middleware function (apply to only endpoint POST /pets)
// Check that the content-type is application/json
// If the content-type is correct, continue to the next middleware
// If the content-type is incorrect, do not continue and send 400 response
Build out the function and make sure that this middleware runs before the middleware that checks for the request’s body. To test this in Postman, you can either set the headers to something like "text/plain" or remove the Content-Type header all together.
Checks for Understanding
- Describe the flow of a middleware function. At what point in the request-response cycle is it run?
- What are some common use cases for using a middleware function?
- What three arguments must be passed into a middleware function?
- How do you apply a middleware function to all endpoints? A single endpoint?